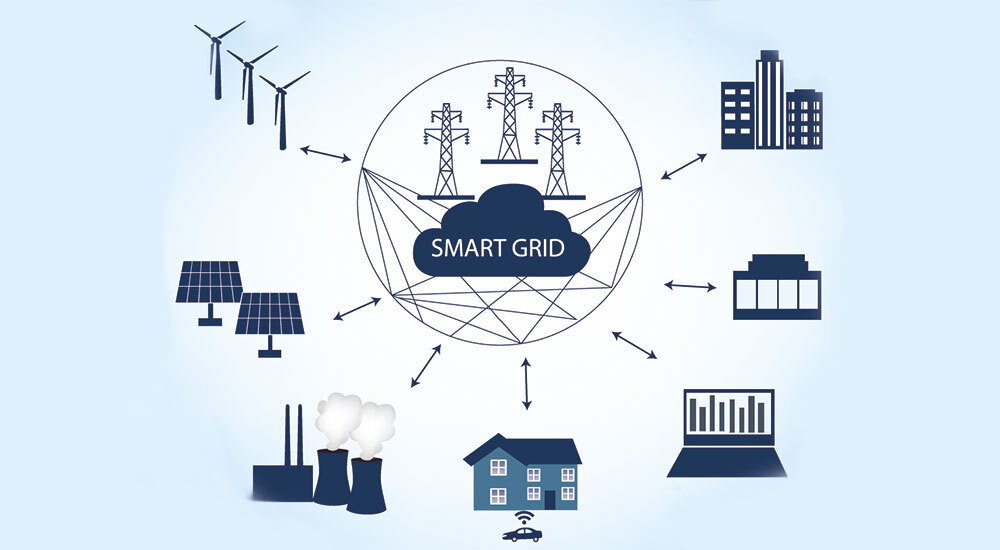
The modern electrical grid is no longer a one-way street. With the influx of distributed energy resources (DERs) like solar panels and EVs, coupled with increasing climate volatility and consumer demand for control, utilities are facing unprecedented complexity. The answer to managing this complexity lies not just in smarter hardware, but in smarter software. Enter the Smart Grid Analytics Market—the critical brain making sense of the grid’s vast nervous system. projected to grow from USD X billion in 2023 to over USD Y billion by 2030 (CAGR of ~Z%), this market is the linchpin of the energy transition.
What is Smart Grid Analytics?
Smart Grid Analytics refers to the application of advanced data processing tools—including Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Big Data platforms—to the massive volumes of data generated by the smart grid. This data comes from smart meters, sensors (PMUs, SCADA), weather feeds, grid equipment, and even customer portals. Analytics transforms this raw data into actionable insights for utilities, grid operators, and consumers.
Key Market Drivers: Why the Surge?
-
The Renewable Energy Imperative: Integrating volatile wind and solar generation requires advanced forecasting and real-time balancing. Analytics predict generation patterns and optimize dispatch.
-
Grid Modernization Investments: Governments worldwide are funding grid resilience projects. Analytics is a core software component of these upgrades, maximizing ROI on new hardware.
-
The Rise of Prosumers: Customers who both consume and produce energy change grid dynamics. Analytics manage two-way power flows, enable virtual power plants (VPPs), and facilitate peer-to-peer energy trading.
-
Demand for Outage Resilience: Climate change increases outage events. Predictive analytics identify failing equipment (like transformers) before they fail, enabling proactive maintenance and faster restoration.
-
Regulatory Pressure & Energy Efficiency: Mandates for reduced losses, improved reliability (SAIDI/SAIFI metrics), and demand response programs are impossible to meet at scale without deep analytical insight.
Market Segmentation: Where is the Intelligence Applied?
The market is typically segmented by:
-
Application:
-
Grid Optimization: Load forecasting, voltage regulation, and loss reduction.
-
Asset Management: Predictive maintenance, health scoring, and lifecycle management.
-
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) Analytics: Theft detection, customer segmentation, and detailed usage insights.
-
Distributed Energy Resource (DER) Management: Integration and optimization of rooftop solar, batteries, and EVs.
-
Risk & Fraud Management: Identifying non-technical losses and cyber-physical threats.
-
-
Deployment Model: Cloud-based (scalable, gaining rapid traction) vs. On-Premise (legacy, security-focused).
-
End-User: Transmission & Distribution Utilities, Renewable Energy Integrators, and Retail Energy Providers.
Dominant Trends Shaping the Future
-
AI & ML Take Center Stage: Moving from descriptive (“what happened”) to prescriptive (“what should we do”) and even autonomous (“self-healing grid”) analytics. AI models are becoming essential for real-time anomaly detection and dynamic pricing.
-
The Edge Computing Shift: To reduce latency and bandwidth, analytics are moving closer to data sources—like substations or even meters—for faster, localized decision-making.
-
Integrated Platforms over Point Solutions: Utilities are seeking unified analytics suites that share data across departments (grid ops, customer service, asset management) over siloed tools.
-
Focus on Cybersecurity Analytics: As grids become more digital, protecting them from attacks is paramount. Analytics continuously monitor network traffic for unusual patterns indicating a breach.
-
Customer-Centric Analytics: Providing consumers with actionable insights on their bills, personalized efficiency tips, and tailored rate plans to enhance engagement and satisfaction.
Check this-
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/chronic-wound-care-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/vinyl-records-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/athletic-shoe-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/adult-incontinence-products-market
https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/de/report/calcium-sulphate-market
Challenges to Overcome
-
Data Silos & Quality: Legacy utility IT systems often trap data in incompatible silos. “Garbage in, garbage out” remains a fundamental hurdle.
-
Skills Gap: A shortage of data scientists and analysts who understand both data tools and power systems.
-
Cybersecurity & Privacy Concerns: Handling vast amounts of sensitive consumption data requires robust protection and clear privacy policies.
-
High Initial Investment & Integration Complexity: Justifying Capex for software and the operational overhaul to use it effectively.
Regional Landscape
-
North America: Leads the market, driven by significant grid modernization investments, supportive policies, and a high penetration of AMI.
-
Europe: A strong follower, propelled by ambitious decarbonization goals (EU Green Deal) and advanced DER integration.
-
Asia-Pacific: The fastest-growing region, fueled by massive smart meter rollouts (e.g., in China and India), rapid urbanization, and investments in renewable energy infrastructure.
The Road Ahead
The Smart Grid Analytics market is evolving from an optional efficiency tool to the essential central nervous system of a reliable, clean, and flexible energy grid. The future winners will be those who treat data as a core asset, break down internal silos, and leverage analytics not just to keep the lights on, but to enable new business models, deepen customer relationships, and accelerate the path to net-zero.
For utilities, the question is no longer if to invest, but how quickly they can build their analytical capabilities to secure their role in the energy ecosystem of tomorrow.